Learn More
Bcl-2 w/control Hamster anti-Human, Unlabeled, Clone: 6C8, BD
Description
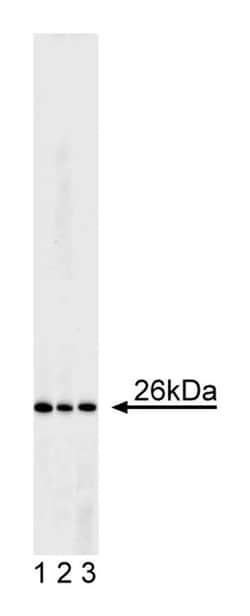
Bcl-2 is considered to be novel among proto-oncogenes because it blocks apoptosis (programmed cell death) in many cell types. Apoptosis is an active form of cellular suicide that typically requires new RNA and protein synthesis and is associated with distinct morphological changes including cell shrinkage, cytoplasm membrane blebbing, nuclear fragmentation and DNA degradation. The Bcl-2 gene was first found in t(14:18) containing follicular B-cell lymphomas. A high proportion of these lymphomas contains t(14:18) chromosomal translocations involving the human Bcl-2 gene. Translocation of Bcl-2 sequences from chromosome 18 onto the transcriptionally active immunoglobulin locus at chromosome band 14q32 in B-cells deregulates Bcl-2 gene expression, resulting in high levels of Bcl-2 mRNA and protein expression. Because Bcl-2 blocks apoptosis, it may contribute to tumorigenesis by prolonged cell survival rather than by accelerating the rate of cell proliferation. The reduced molecular weight of Bcl-2 is 26 kDa. Additional minor bands at 27-31 kDa and 18-21 kDa may also be observed.

Specifications
Specifications
| Antigen | Bcl-2 w/control |
| Applications | Western Blot |
| Classification | Monoclonal |
| Clone | 6C8 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Host Species | Hamster |
| Purification Method | Affinity Purified |
| Quantity | 50 μg |
| Regulatory Status | RUO |
| Primary or Secondary | Primary |
| Show More |
For Research Use Only.
By clicking Submit, you acknowledge that you may be contacted by Fisher Scientific in regards to the feedback you have provided in this form. We will not share your information for any other purposes. All contact information provided shall also be maintained in accordance with our Privacy Policy.